Structural principle and technical advantages of plate heat exchanger
Jul 25,2024
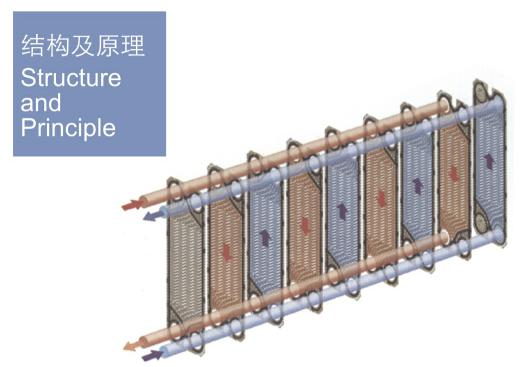
The plate heat exchanger is composed of a plurality of corrugated heat transfer plate groups sandwiched between the top beam of the upper bracket and the lower support beam. The waveform of the heat transfer plates that forms a flow path through which the two media pass makes the fluid turbulent and supports the plates by the pressure difference between the two fluids. The heat transfer plate set is fastened with clamping bolts and nuts between the fixed hold-down plate and the mobile hold-down plate.
Principle
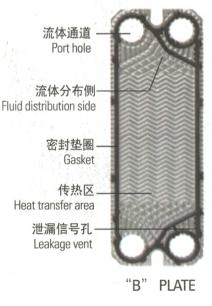
The heat transfer plate is equipped with a sealing gasket, which forms a flow channel and acts as a sealing to prevent liquid leakage. The number and size of heat transfer plates depend on the flow rate of the medium, the physical properties of the fluid, the pressure drop, and the temperature conditions at the inlet and outlet. The main purpose of the compression plate is to prevent the deformation of the plate that may be caused by the difference in fluid pressure.
When assembling the heat transfer plates (plates with sealing washers), the plate faces with the sealing gaskets are oriented towards the hold-down plates, and each plate is rotated 180 degrees to form a flow channel. Liquids that flow only along plate A always flow inside plate A: liquids that flow only along plate B flow in the opposite direction within each other plate mounted.

Technical advantages
1. Unique plate grid guide area design (patent number: ZL 2009 2 0153477.8)
2. Positioning and interlocking between plates with excellent performance (Patent No.: ZL 2009 2 0153478.2)
3. Suspension system of plate heat exchanger:
4. Rich plate family
5. Advanced sealing structure
6. Precision plate processing and mold processing
7. Advanced disassembly and assembly structure
8. Professional process calculation software

Plate type
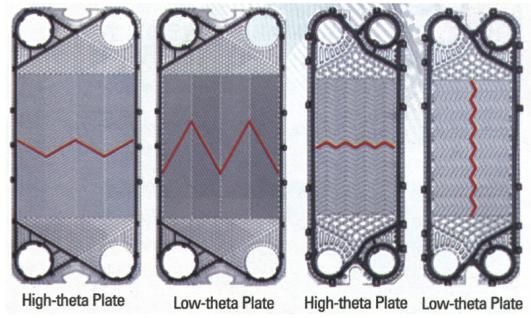
Large angle plates
●(High turbulent flow)
●(high heat transfer coefficient)
●(Perfect temperature approach)
●(High pressure drop)
Small angle plates
●(Low turbulent flow)
●(Low heat transfer coefficient)
●(High temperature approach)
●(Low pressure drop)
Channel combinations
It consists of three channel combinations: a large-angle plate and a small-angle plate
High-impedance channels
A combination of two large angle plates
Low-impedance channel
A combination of two small angle plates
Medium resistance channel
A combination of a large angle plate and a small angle plate
PREVIOUS:
NEXT:






